Embracing a Brighter, Greener Future
Welcome to the Vital Mag blog, where we dive into the cool and ever-changing world of renewable energy! Imagine a future where our homes and cities are powered by the wind, sun, and water, all while keeping our planet happy and healthy. That future is closer than you think, and it’s full of exciting new ideas and gadgets. From sleek solar panels that capture more sunlight to wind turbines spinning in new ways, renewable energy is like a high-tech superhero for our environment. Join us as we explore the innovations making waves and see how they’re changing the game for everyone. Whether you’re a green energy newbie or a seasoned pro, there’s something here that’ll spark your curiosity and keep you inspired. Let’s jump in and see what’s lighting up the world of renewable energy today!
The Future of Renewable Energy: Innovations and Impacts

Emerging Technologies Shaping Renewable Energy
The renewable energy landscape is undergoing a transformative shift driven by cutting-edge technologies. One of the most promising advancements is in the realm of solar photovoltaic systems. Next-generation solar panels are becoming more efficient, with researchers developing materials that enhance light absorption and increase energy conversion rates. This leap in technology is not only improving performance but also reducing the cost per watt of solar energy, making it a more accessible option for both residential and commercial applications.
Wind energy is also seeing significant technological progress. Innovations in turbine design, such as larger and more aerodynamic blades, are enabling turbines to capture more wind and generate electricity even at lower wind speeds. Additionally, floating wind farms are emerging as a viable solution for harnessing wind energy in deep water locations previously deemed impractical. These advancements are expanding the potential of wind energy to new geographical regions and contributing to a more diverse renewable energy portfolio.
Energy storage technologies are crucial for balancing supply and demand in renewable energy systems. Recent developments in battery technology, particularly solid-state batteries, promise greater energy density and faster charging times compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This improvement not only enhances the efficiency of energy storage but also extends the lifespan of battery systems, making renewable energy sources more reliable and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.

The Economic Benefits of Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy is proving to be a catalyst for economic growth on multiple fronts. One of the primary economic benefits is job creation. The renewable energy sector has seen a surge in employment opportunities across various disciplines, including manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of renewable energy systems. This trend is expected to continue as the sector expands, creating a diverse range of high-quality jobs and supporting local economies.
Renewable energy also offers significant savings on energy costs over the long term. While the initial investment in renewable energy infrastructure can be substantial, the reduction in operating costs and energy bills provides a favorable return on investment. For instance, solar and wind energy systems often have lower maintenance costs compared to conventional fossil fuel-based power plants, leading to ongoing savings for businesses and homeowners alike.
Furthermore, the renewable energy sector is driving economic diversification and resilience. By reducing reliance on imported fuels and creating a robust domestic energy infrastructure, countries can mitigate the economic impacts of volatile fossil fuel prices. This strategic shift not only strengthens national energy security but also stimulates economic activity and innovation within the renewable energy sector itself.

The Role of Policy in Accelerating Renewable Energy Adoption
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping the future of renewable energy by creating a favorable environment for investment and innovation. Incentive programs, such as tax credits and subsidies, are instrumental in reducing the financial barriers associated with adopting renewable energy technologies. These incentives help offset the initial costs and encourage both individuals and businesses to transition to cleaner energy sources.
Regulatory frameworks also influence the pace of renewable energy adoption. Streamlined permitting processes and supportive regulations can facilitate the deployment of renewable energy projects. For example, policies that prioritize grid integration and provide clear guidelines for interconnection can accelerate the development of renewable energy infrastructure and ensure that new projects are integrated efficiently into existing energy systems.
International agreements and collaborations further bolster renewable energy efforts by setting global targets and fostering cross-border partnerships. Agreements such as the Paris Agreement commit countries to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable energy practices. By working together and sharing knowledge, countries can collectively advance renewable energy technologies and achieve their climate goals more effectively.

The Environmental Impact of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources are heralded for their minimal environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuels. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gasses, thus playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change. This shift towards cleaner energy sources helps reduce air and water pollution, contributing to healthier ecosystems and communities.
However, it is important to recognize that renewable energy technologies are not without their environmental considerations. For instance, the production of solar panels and wind turbines involves the use of raw materials and energy, which can have ecological implications. Additionally, large-scale renewable energy projects, such as hydroelectric dams, may affect local wildlife and habitats. Therefore, it is essential to approach the deployment of renewable energy technologies with a balanced perspective, considering both their benefits and potential environmental impacts.
Efforts to minimize the environmental footprint of renewable energy are ongoing. Innovations in recycling and resource efficiency are helping to reduce the ecological impact of manufacturing and disposing of renewable energy technologies. By incorporating sustainable practices and continuous improvement, the renewable energy sector aims to enhance its environmental performance and contribute positively to the planet’s long-term health.
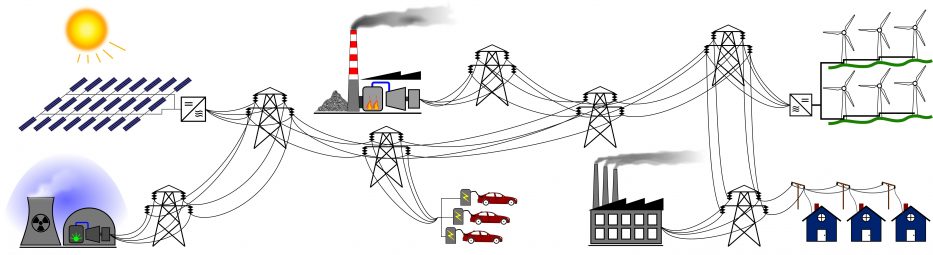
The Future Prospects of Renewable Energy Integration
As renewable energy technologies advance, their integration into the existing energy infrastructure presents both opportunities and challenges. One of the key prospects is the development of smart grids, which use advanced digital technologies to optimize the distribution and management of electricity. Smart grids can accommodate a higher share of renewable energy by improving grid reliability and enabling better demand response.
The concept of energy decentralization is also gaining traction, with the rise of microgrids and localized energy systems. These smaller, self-sufficient energy networks can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing greater resilience and flexibility. By enabling communities to generate and manage their own renewable energy, these systems offer a pathway to enhanced energy security and sustainability.
As sustainable energy solutions continue to advance, embracing a brighter, greener future becomes imperative. The future of renewable energy lies in the progress of solar and wind advancements, which have the potential to make a significant impact. By integrating smart grids and decentralizing energy systems, we can harness green energy innovations and reap the benefits of renewable energy, such as improved grid reliability, better demand response, enhanced energy security, and long-term sustainability.



